If you've spent any time in fitness or nutrition circles, you've likely heard people talking about "counting macros" or "hitting their macros." But what exactly are macros, why do they matter, and how can you use them to improve your health? This beginner's guide will break down everything you need to know about macronutrients and how Sugar Ai can help you track them effortlessly.
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients (or "macros" for short) are the three main categories of nutrients that provide energy to your body: proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Unlike micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) that your body needs in small amounts, macronutrients are required in larger quantities and make up the bulk of your diet.
Each macronutrient serves different functions in your body and provides different amounts of energy:
- Protein: 4 calories per gram
- Carbohydrates: 4 calories per gram
- Fat: 9 calories per gram
Now, let's explore each macronutrient in more detail.
Protein: The Building Block
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, including muscles, organs, and skin. It also plays a crucial role in enzyme and hormone production, immune function, and cellular communication.
Key Benefits of Protein:
- Builds and repairs muscle tissue
- Increases satiety (feeling of fullness)
- Requires more energy to digest than other macros (thermic effect)
- Helps maintain muscle mass during weight loss
- Stabilizes blood sugar levels
Good Sources of Protein:
- Animal sources: Chicken, turkey, beef, fish, eggs, dairy
- Plant sources: Tofu, tempeh, legumes, quinoa, nuts, seeds
- Supplements: Whey, casein, pea, rice, and hemp protein powders
Protein Tip
For general health, aim for 0.8-1g of protein per pound of body weight if you're physically active. If you're sedentary, 0.5-0.7g per pound is typically sufficient.
Carbohydrates: The Energy Provider
Carbohydrates are your body's preferred energy source, especially for high-intensity activities and brain function. When you consume carbs, your body breaks them down into glucose, which can be used immediately for energy or stored as glycogen in your muscles and liver for later use.
Key Benefits of Carbohydrates:
- Provide quick energy for physical activities
- Fuel brain function and cognitive processes
- Spare protein for tissue building rather than energy
- Support digestive health (fiber)
- Enable proper functioning of the central nervous system
Types of Carbohydrates:
Not all carbs are created equal. They can be categorized based on their structure and how they affect your body:
- Simple carbs: Quickly digested sugars found in fruits, milk, and refined foods
- Complex carbs: Longer chains of sugars that take longer to digest, found in whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables
- Fiber: A type of carbohydrate that your body can't digest, which supports digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar
Good Sources of Carbohydrates:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley
- Starchy vegetables: Sweet potatoes, potatoes, corn, peas
- Fruits: Apples, bananas, berries, oranges
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas
Carb Tip
Focus on fiber-rich, minimally processed carbohydrates most of the time. These provide sustained energy and more nutrients than their refined counterparts.
Fats: The Essential Nutrient
Despite getting a bad reputation in the past, dietary fats are essential for your health. They support cell structure, hormone production, vitamin absorption, and provide a concentrated source of energy.
Key Benefits of Fats:
- Provide energy, especially during low-intensity activities
- Support cell membrane structure and function
- Aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
- Contribute to hormone production
- Provide insulation and organ protection
- Enhance flavor and satiety in meals
Types of Fats:
- Unsaturated fats: Generally considered heart-healthy, found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish
- Saturated fats: Found in animal products and some plant oils (coconut, palm); moderation is recommended
- Trans fats: Mostly artificial fats found in processed foods; best avoided
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Essential fats with anti-inflammatory properties, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts
Good Sources of Healthy Fats:
- Avocados
- Olive oil, avocado oil
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Eggs (especially the yolks)
- Full-fat yogurt
Fat Tip
Don't fear fat, but choose your sources wisely. Aim for a mix of monounsaturated, polyunsaturated (including omega-3s), and some saturated fats from quality sources.
Why Balance Matters
While each macronutrient is important individually, the balance between them is what truly matters for overall health and specific goals. Different macro ratios can support different objectives:
- General health: Balanced approach with adequate amounts of all three macros
- Weight loss: Often higher protein, moderate fat, lower carb
- Athletic performance: Usually higher carb, moderate protein, lower fat
- Muscle building: Higher protein, higher carb, moderate fat
There's no one-size-fits-all approach to macro ratios. Your ideal balance depends on your individual factors like age, sex, activity level, goals, and even genetics.
How Sugar Ai Helps You Track Macros
Traditionally, tracking macros involved weighing food, reading labels, and manually logging everything you eat. Sugar Ai simplifies this process dramatically:
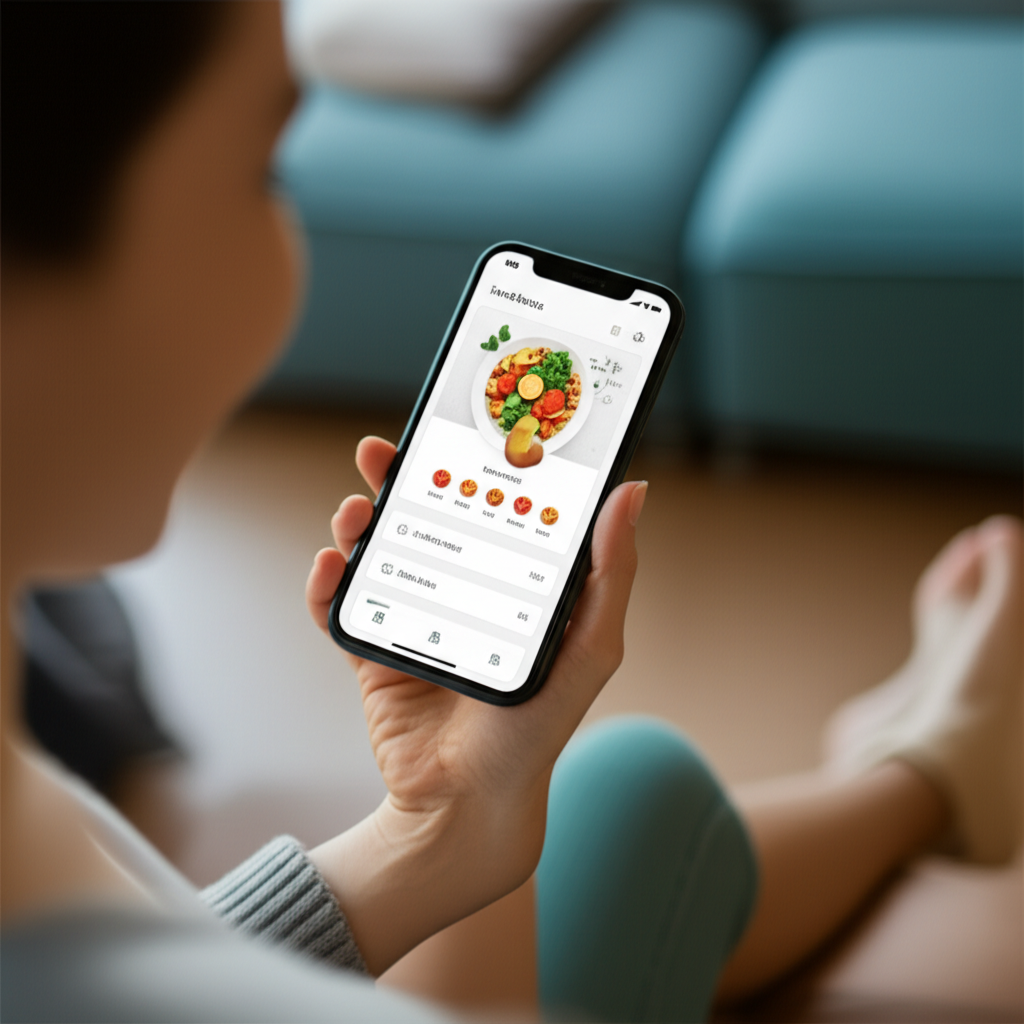
- Visual Recognition: Simply take a photo of your meal, and Sugar Ai identifies the foods
- Automatic Calculation: The app automatically calculates the protein, carbs, and fat in your meal
- Daily Tracking: See your macro intake throughout the day and how it compares to your targets
- Trend Analysis: Review patterns over time to understand how your macro balance affects your energy, mood, and progress
- Personalized Recommendations: Receive suggestions for adjusting your macro intake based on your goals and responses
With Sugar Ai, you can understand your macro intake without the tedious work of manual tracking. This makes it easier to make informed choices and adjust your diet as needed.
Getting Started with Macro Tracking
If you're new to tracking macros, here are some steps to get started:
- Determine your goals: Weight loss, maintenance, muscle gain, athletic performance, etc.
- Calculate your baseline needs: Use Sugar Ai's calculator or consult with a nutrition professional
- Start tracking: Use Sugar Ai to photograph and log your meals
- Observe and adjust: Pay attention to how different macro balances affect your energy, hunger, and performance
- Be consistent but flexible: Aim for consistency over perfection, and adjust your approach based on results
Remember that macro tracking is a tool, not a rule. It's meant to help you understand your nutrition better and make informed choices, not to create stress or rigid eating patterns.
Beyond the Numbers
While tracking macros can be incredibly useful, it's important to remember that quality matters as much as quantity. Two meals with identical macro profiles can have vastly different effects on your body depending on the quality of the foods and their micronutrient content.
Sugar Ai helps you go beyond simple macro counting by providing insights into the overall nutritional quality of your meals, including micronutrients and food quality factors.